you buy a 8% coupon, 10-year maturity bond for 980. what is the new yield to maturity on the bond
What is Coupon Bond Formula?
The term "coupon bond Coupon bonds pay stock-still interest at a predetermined frequency from the bond'southward consequence engagement to the bond's maturity or transfer date. The holder of a coupon bond receives a periodic payment of the stipulated fixed interest charge per unit. read more " refers to bonds that pay coupons which is a nominal percentage of the par value or chief corporeality of the bond. The formula for calculation of the price of this bond basically uses the present value of the probable future cash flows in the form of coupon payments and the chief amount which is the amount received at maturity. The nowadays value is computed by discounting the greenbacks flow using yield to maturity.
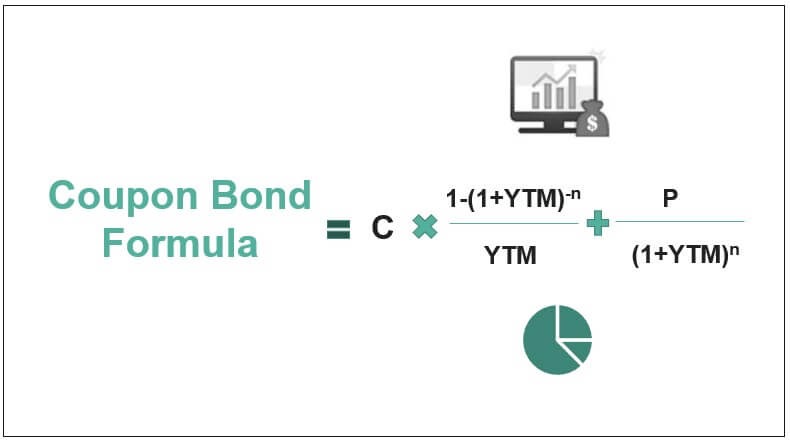
Mathematically, it the price of a coupon bond The bond pricing formula calculates the present value of the probable future cash flows, which include coupon payments and the par value, which is the redemption amount at maturity. The yield to maturity (YTM) refers to the charge per unit of interest used to discount hereafter cash flows. read more is represented equally follows,
Coupon Bond = ∑i=1 north [C/(1+YTM)i + P/(ane+YTM)n]
Coupon Bail = C * [1-(1+YTM)-n/YTM + P/(one+YTM)northward]
You are free to utilise this prototype on your website, templates etc, Delight provide us with an attribution link Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Coupon Bond Formula (wallstreetmojo.com)
where
- C = Periodic coupon payment,
- P = Par value of bail,
- YTM = Yield to maturity The yield to maturity refers to the expected returns an investor anticipates later keeping the bond intact till the maturity date. In other words, a bond's returns are scheduled after making all the payments on time throughout the life of a bond. Dissimilar current yield, which measures the present value of the bond, the yield to maturity measures the value of the bond at the cease of the term of a bond. read more
- n = No. of periods till maturity
Calculation of the Coupon Bond (Step by Step)
The formula for coupon bond adding tin can be washed past using the following steps:
- Firstly, determine the par value of the bond issuance, and it is denoted by P.
- Next, determine the periodic coupon payment based on the coupon rate of the bond based, the frequency of the coupon payment, and the par value of the bond. The coupon payment is denoted by C, and information technology is calculated as C = Coupon rate * P / Frequency of coupon payment
- Side by side, decide the total number of periods till maturity by multiplying the frequency of the coupon payments during a year and the number of years till maturity. The number of periods till maturity is denoted by northward, and it is calculated equally, due north = No. of years till maturity * Frequency of coupon payment
- Now, determine the yield to maturity The yield to maturity refers to the expected returns an investor anticipates later on keeping the bond intact till the maturity engagement. In other words, a bail's returns are scheduled after making all the payments on time throughout the life of a bond. Unlike current yield, which measures the present value of the bond, the yield to maturity measures the value of the bond at the end of the term of a bond. read more on the footing of the electric current marketplace return from an investment with a similar risk contour. The yield to maturity is denoted by YTM.
- Side by side, determine the nowadays value of the first coupon, 2d coupon, and so on. And then, determine the present value of the par value of the bond.
- Finally, the formula for determination of the coupon bond calculation is done by adding the present value of all the coupon payments and the par value, every bit shown below.

Examples
You can download this Coupon Bond Formula Excel Template hither – Coupon Bond Formula Excel Template
Example #1
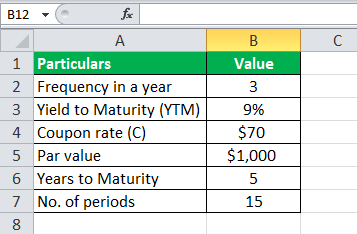
Let united states of america take an case of bonds issued by company XYZ Ltd that pays coupons annually. The company plans to issue 5,000 such bonds, and each bond has a par value of $1,000 with a coupon rate of 7%, and information technology is to mature in 15 years. The effective yield Constructive yield is a yearly charge per unit of return at a periodic interest charge per unit proclaimed to be one of the effective measures of an equity holder'due south render as it takes compounding into its due consideration, different the nominal yield method. read more than to maturity is 9%. Determine the cost of each bail and the money to exist raised by XYZ Ltd through this bail upshot.
Beneath is given information for the adding of the coupon bond of XYZ Ltd.
The price of each bond is calculated using the below formula equally,

Therefore, calculation of the Coupon Bond will be every bit follows,
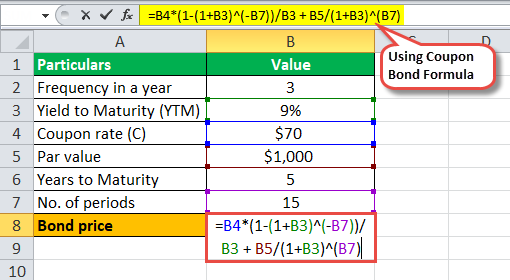
And so information technology will exist –
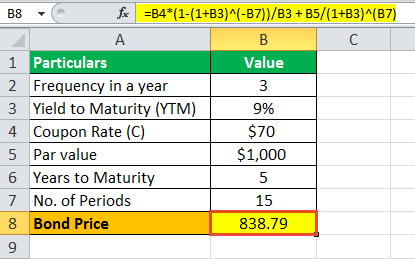
= $838.79
Therefore, each bond will be priced at $838.79 and said to exist traded at a disbelieve (bail price lower than par value) considering the coupon rate The coupon charge per unit is the ROI (rate of involvement) paid on the bond'due south confront value by the bond'southward issuers. It determines the repayment amount fabricated by GIS (guaranteed income security). Coupon Rate = Annualized Involvement Payment / Par Value of Bond * 100% read more is lower than the YTM. XYZ Ltd volition be able to heighten $iv,193,950 (= 5,000 * $838.79).
Instance #2
Let us have an instance of bonds issued by company ABC Ltd that pays semi-annual coupons. Each bail has a par value of $i,000 with a coupon rate of 8%, and information technology is to mature in 5 years. The effective yield to maturity is 7%. Determine the price of each C bond issued past ABC Ltd.
Below is given data for the calculation of the coupon bond of ABC Ltd.

Therefore, the price of each bond can be calculated using the below formula every bit,

Therefore, calculation of the Coupon Bond will be as follows,

So information technology volition be –
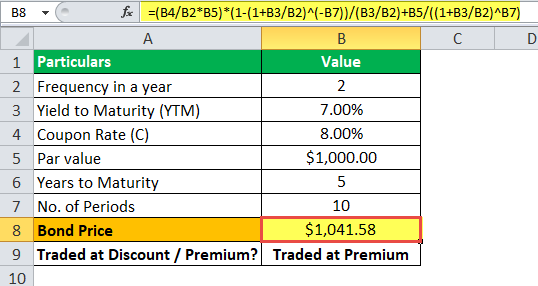
= $one,041.58
Therefore, each bail will exist priced at $1,041.58 and said to exist traded at a premium (bond cost higher than par value) because the coupon rate is college than the YTM.
Relevance and Uses
The concept of pricing of this kind of bond is very important from the perspective of an investor because bonds are an indispensable office of the upper-case letter markets. The purchaser of a bond receives these coupon payments during the period between the issuance of the bond and the maturity of the bail. In the bond market, bonds with higher coupon rates are considered to be more attractive for investors because they offering higher yields.
Further, bonds trading at a value higher than their par value is said to be traded at a premium, while the bonds trading at a value lower than their par value is said to be traded at a disbelieve. Nowadays, these bonds are quite uncommon considering most recent bonds are not issued in coupon or certificate form. Rather the bonds Bonds refer to the debt instruments issued by governments or corporations to acquire investors' funds for a certain period. read more than are issued electronically.
Recommended Manufactures
This has been a guide to Coupon Bond Formula. Here we discuss how to calculate the Price of a Coupon Bond forth with the examples and downloadable excel template. You may learn more than about excel from the following manufactures –
- Par Value of Share Formula
- Zippo-Coupon Bond
- Bond Pricing Formula Adding
- Examples of Duration Formula
- ix Courses
- 37+ Hours
- Total Lifetime Access
- Certificate of Completion
LEARN More >>
Source: https://www.wallstreetmojo.com/coupon-bond-formula/
0 Response to "you buy a 8% coupon, 10-year maturity bond for 980. what is the new yield to maturity on the bond"
Post a Comment